How To Find Two Missing Angles In A Triangle | Sal is given a right triangle with an acute angle of 65° and a leg of 5 units, and he uses trigonometry to find the two missing sides. Angles angles outside the two lines and on Such a triangle can be solved by using angles of a triangle to find the other angle, and the law of sines to find each of the other two sides. This means we are given two angles of a triangle and one side, which is the side adjacent to the two given angles. Find lengths a and b of triangle s.
We know all the sides in triangle r, and we know the side 6.4 in triangle s. In this case we find the third angle by using. If the known angle is opposite a marked side, then the angle opposite the other marked side is the same. So we can match 6.4 with 8, and so the ratio of sides in triangle s to triangle r is: If two sides are given, the pythagoras theorem can be used and when the measurement of one side and an angle is given, trigonometric functions like sine, cos, and tan can be used to find the missing side.
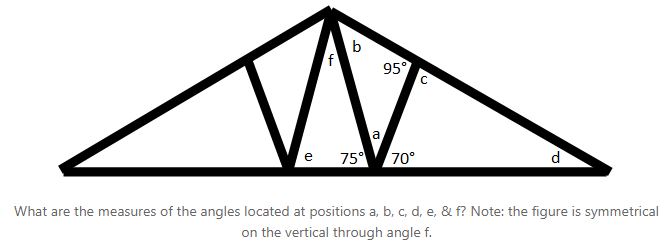
The 6.4 faces the angle marked with two arcs as does the side of length 8 in triangle r. Add these two angles together and subtract the answer from 180° to find the remaining third angle. This means we are given two angles of a triangle and one side, which is the side adjacent to the two given angles. So we can match 6.4 with 8, and so the ratio of sides in triangle s to triangle r is: In this case we find the third angle by using. O an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. We know all the sides in triangle r, and we know the side 6.4 in triangle s. Sal is given a right triangle with an acute angle of 65° and a leg of 5 units, and he uses trigonometry to find the two missing sides. Oct 13, 2018 · if only one angle is known in an isosceles triangle, then we can find the other two missing angles using the following steps: Such a triangle can be solved by using angles of a triangle to find the other angle, and the law of sines to find each of the other two sides. An equilateral triangle has 3 equal angles that are 60° each. Find lengths a and b of triangle s. Angles angles outside the two lines and on
So we can match 6.4 with 8, and so the ratio of sides in triangle s to triangle r is: The 6.4 faces the angle marked with two arcs as does the side of length 8 in triangle r. We know all the sides in triangle r, and we know the side 6.4 in triangle s. An equilateral triangle has 3 equal angles that are 60° each. Find lengths a and b of triangle s.
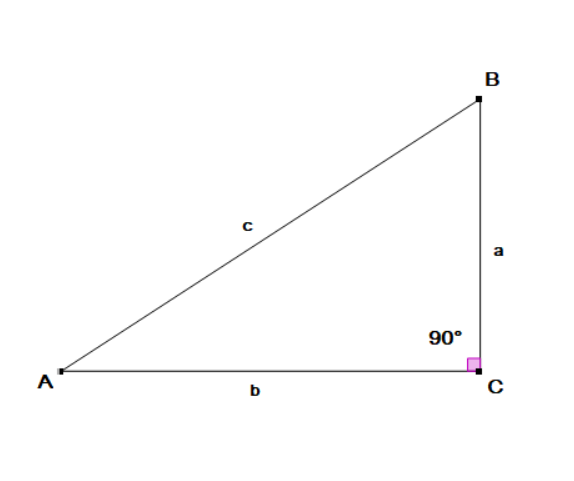
Oct 13, 2018 · if only one angle is known in an isosceles triangle, then we can find the other two missing angles using the following steps: An equilateral triangle has 3 equal angles that are 60° each. Add these two angles together and subtract the answer from 180° to find the remaining third angle. The 6.4 faces the angle marked with two arcs as does the side of length 8 in triangle r. If two sides are given, the pythagoras theorem can be used and when the measurement of one side and an angle is given, trigonometric functions like sine, cos, and tan can be used to find the missing side. Find lengths a and b of triangle s. In this case we find the third angle by using. So we can match 6.4 with 8, and so the ratio of sides in triangle s to triangle r is: Such a triangle can be solved by using angles of a triangle to find the other angle, and the law of sines to find each of the other two sides. Sal is given a right triangle with an acute angle of 65° and a leg of 5 units, and he uses trigonometry to find the two missing sides. We know all the sides in triangle r, and we know the side 6.4 in triangle s. O an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. If the known angle is opposite a marked side, then the angle opposite the other marked side is the same.
Such a triangle can be solved by using angles of a triangle to find the other angle, and the law of sines to find each of the other two sides. Find lengths a and b of triangle s. This means we are given two angles of a triangle and one side, which is the side adjacent to the two given angles. Oct 13, 2018 · if only one angle is known in an isosceles triangle, then we can find the other two missing angles using the following steps: The 6.4 faces the angle marked with two arcs as does the side of length 8 in triangle r.
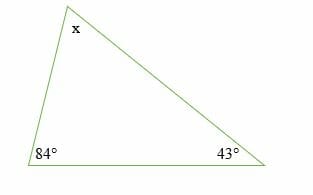
Oct 13, 2018 · if only one angle is known in an isosceles triangle, then we can find the other two missing angles using the following steps: So we can match 6.4 with 8, and so the ratio of sides in triangle s to triangle r is: O an equilateral triangle inscribed in a circle. An equilateral triangle has 3 equal angles that are 60° each. Add these two angles together and subtract the answer from 180° to find the remaining third angle. This means we are given two angles of a triangle and one side, which is the side adjacent to the two given angles. Such a triangle can be solved by using angles of a triangle to find the other angle, and the law of sines to find each of the other two sides. In this case we find the third angle by using. We know all the sides in triangle r, and we know the side 6.4 in triangle s. If the known angle is opposite a marked side, then the angle opposite the other marked side is the same. Sal is given a right triangle with an acute angle of 65° and a leg of 5 units, and he uses trigonometry to find the two missing sides. The 6.4 faces the angle marked with two arcs as does the side of length 8 in triangle r. If two sides are given, the pythagoras theorem can be used and when the measurement of one side and an angle is given, trigonometric functions like sine, cos, and tan can be used to find the missing side.
How To Find Two Missing Angles In A Triangle: If the known angle is opposite a marked side, then the angle opposite the other marked side is the same.
0 Tanggapan:
Post a Comment